Contents in this Page
Executive Summary
This post is about the External business environment of DHL. Auditing the external environment provides a company with an excellent opportunity to assess the threats and competitive environment of the business. Contemporary business concepts such as knowledge management significantly impact a business if it utilizes the benefits the subject offers. This report has critically applied the above two issues to a logistics company: DHL. It has been found in the report that DHL is a global company having operations in 220 countries. Since it has operations worldwide, it has to face a diversified number of critical situations related to culture, political environment, and economic environment. It has been found in the report that the global political environment and economic ups and downs across countries affect the company most intensively. It has also been found that the political environment, technological environment, the ecological environment also play a role in affecting DHL to act in a certain way. PESTEL and Porter’s Five Forces Model have found that DHL faces fewer threats for new entrants because this is a high-value invested industry and new entrants pose a minimum risk for a big giant like DHL. The report has also found that buyers have less bargaining power because of the superior and differentiated services DHL provides. In the second part of the report, it has been found that knowledge management plays a significant role in a technology-based company DHL. The company inspires the employees to learn new technologies, strategies, approaches and ways to facilitate growth. The company also inspires employees to share their knowledge. It has been found that knowledge sharing has fostered growth in DHL.
Introduction
Concepts of contemporary development have been applied in this report. For the purpose of the application, DHL has been selected. External business environment of DHL will be analysed in this article. This report is divided into two tasks. In the first part of the report, a PESTLE analysis has been conducted on DHL to evaluate the impact of external factors on their business and Porter’s five forces model has been applied to know about the competition that DHL faces in the industry. In the second part of this report, the relevance of knowledge management toward DHL has been evaluated, and the effectiveness of knowledge management in the operations of the company has also been evaluated. And some recommendations for DHL have been stated in the last segment of task two.
Assessment of the impact of external business environmental factors on DHL and its responses
PESTLE Analysis of DHL
PESTLE analysis is the framework used by companies to know about the impact of all the external environments on their business operations; therefore, companies can take significant initiatives to minimize the impacts (Rastogi, and Trivedi, 2016). Political, economic, social, technological, legal and ecological are the six environments of PESTLE analysis that influence the business activities of all companies. PESTLE analysis of DHL is analysed below:
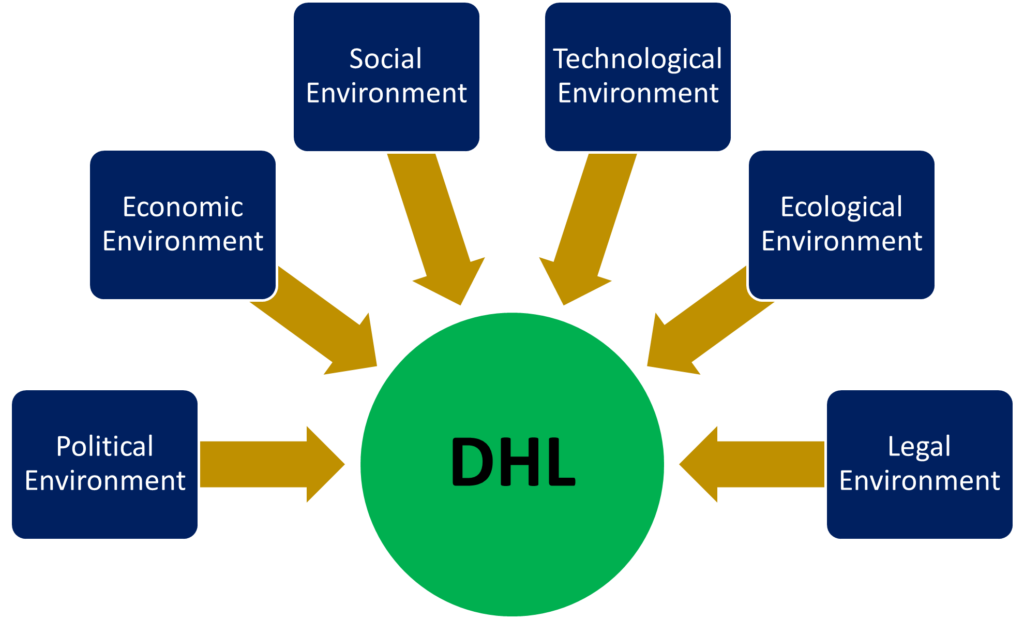
Political Environment: Political environment analysis refers to the impact of political factors on a company’s business operations. Companies become aware of minimizing the negative impact of the factors by analysing the political environment (SHTAL et al., 2018). The political environment of those 220 countries of the world in which DHL provides its services are different from one another and influence their operations (DHL, 2020). For instance, South Asian countries such as Pakistan and Bangladesh have unstable political environments and frequently change trade policies, creating problems for DHL (Herold, and Lee, 2017). The changing trade policies of the countries increase the policy implementation costs of DHL because the company has to adopt changes in its policies according to the countries’ trade policies. As a result, the profit level of DHL decreases in the countries.
Economic Environment: Economic environment analysis shows the effect of the economic factors and organizations can take significant steps to handle the effect of the factors in their business procedures (Aithal, 2016). The inflation rate, GDP growth, bank rate, employment rate, recession, etcetera are the economic factors that influence the actions of DHL. For instance, the GDP of China is 13.4 trillion, which refers to the Chinese’s financial stability, and the company’s people afford DHL’s services efficiently (World Population View, 2020). Apart from the above, world GDP is increasing yearly due to increased economic activities. As a result, DHL will get more business every year.
Social Environment: By analysing the social environment, organizations become aware of the influence of the social factors on their business, and they can take effective steps to avoid the effects of the environment (Islam, and Mamun, 2017). For instance, Saudi Arabia has a higher distance in hierarchical relationships in management structure; therefore, DHL adjusts its business management practices in the country. Another social factor is the increased demand for online services has compelled DHL to ensure its presence in the online service sector. It has increased the demand for DHL because customers can get their service from anywhere.
Technological Environment: Technological environment refers to the condition of science and technology; therefore, companies can adopt appropriate technology to ensure the growth of their business (Düerkop, and Huth, 2017). DHL has utilized the development of communication technologies and conducted social media marketing (Al-Salami et al., 2019). It helps DHL to minimize marketing costs because they can stay connected with their customers across the world. The company conducts creative social media campaigns that assist them in developing online brand communities. DHL conduct ongoing technical innovations to deliver the best customer experience.
Legal Environment: Companies can become aware of the attitude of government toward business, trends of public control in taxation, rules of commerce and competition, antitrust rules, etcetera by analysing the legal environment that help DHL to act in the right way to prevent legal complexities in business (Christodoulou, and Cullinane, 2019). DHL maintains the employee protection law, consumer protection laws, intellectual property law and other laws to act their business in the right way and avoid penalties from governments of host countries. For instance, DHL maintains labour health and safety laws and ensures employee protection.
Ecological Environment: Ecological environment analysis assists in identifying the effect of natural disasters on a business and how business operations affect the global environment (Moro Visconti, 2016). DHL has Disaster Response Team (DRT) volunteers who are well trained and coordinate relief logistics to ensure the proper relief distribution (Deutsche Post DHL Group, 2020). The team plays an outstanding role in reaching relief to NGOs or communities. These steps increase the reputation of DHL across the world.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of DHL
Porter’s five forces are the model that helps companies to get informed about the competition in the market they operate the business, and companies can strengthen their position by knowing about the competition in the market. Porter’s five forces model of DHL has been stated below:
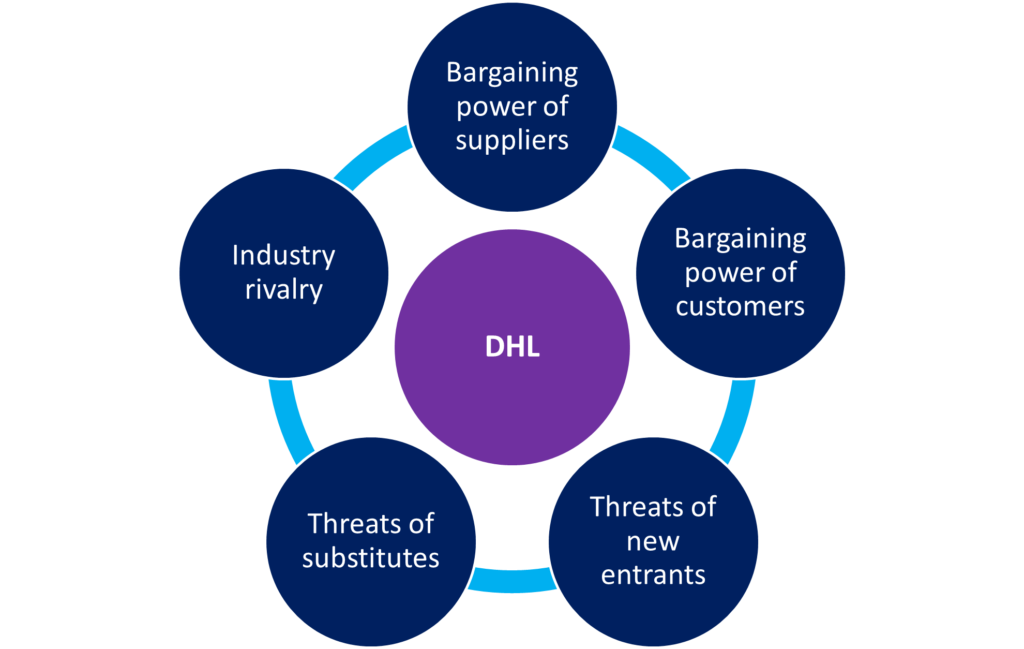
Threats of new entry: Threats of new entry are weaker for DHL because the company’s product differentiation is strong, and the company is customers’ number one choice (Oflac et al., 2015). DHL’s economies of scale help them to produce large capacity with a cost advantage, which is costlier for new entrants, and they will not be capable of producing the large capacity. New entrants will need higher capital to set up business in the industry where DHL is one of the leading companies; therefore, new entrants will not be able to replace DHL easily.
Threats of substitutes: Threats of substitutes for DHL are low because very few substitutes are available in the industry (Bagalwadi, 2015). The substitutes of DHL are less authentic and reliable. Whilst, DHL sells at a lower price than the substitutes with satisfactory quality, which brings most of the buyers toward DHL, and the company gets most of the customers of the industry. The satisfactory quality of reasonable prices makes the threat of substitutes weaker.
Power of suppliers: There are a lot of suppliers (they include technical support providers, logistic support providers, materials suppliers etc.) available in the industry to which DHL belongs, and this makes suppliers less powerful in the industry (MacGillavry, and Sinyan, 2016). Because of lot availability of suppliers in the industry, the switching cost is lower; therefore, DHL can switch to other suppliers at any time. If any suppliers want to bargain with DHL, they can easily switch to others easily. For that reason, suppliers cannot control the price of products and provides products with reasonable price and good quality for DHL.
Power of buyers: There are fewer substitutes for DHL products which makes the bargaining power of buyers weaker because they have few options to choose from and cannot control the price by bargaining (Wziątek-Staśko, and Chabińska-Rossakowska, 2015). The industry keeps differentiating its products, and DHL invests more in R&D to differentiate. Therefore, customers can hardly find a specific service in another firm that also compels customers to choose DHL products because the company always provides highly differentiated products.
The intensity of rivalry: FedEx, SAAM, Royal Mail, United Parcel Service etcetera are the major competitors of DHL (Craft, 2020). The number of competitors in the industry is less, but the competitors are big in size. All of them take different types of competitive actions to have more market share, which refers to the strong competition in the industry for DHL.
Recommendations for DHL:
Firstly, DHL has to take steps after considering the political environment of those 220 host countries they have services, in order to adapt to the country’s political environment (Żurek, Ziółkowski, and Szkutnik-Rogoż, 2019). It will ensure that governments of the countries will not interfere in the business operations of DHL, and the company will be capable of operating its business with fewer complexities.
Secondly, DHL should focus on their marketing process because there are many people across the world who do not know about the company (Ramnath, 2017). The competitors of DHL conduct both traditional and digital marketing to increase their publicity. DHL should also conduct both traditional and digital marketing to increase its publicity across the world.
Thirdly, the company should focus on providing online services because the demand for online logistics services has increased greatly (Dhir, 2019). Customers will get the services of DHL anywhere, and they will not need to visit the offices of DHL; therefore, it will increase the sales of the company enormously at the present time.
Fourthly, DHL should carry on investing in the R&D sector to adopt new innovative services and keep them differentiated from its competitors (Polina, 2016). It will maintain the uniqueness of the services of DHL that will maintain their customers and furthermore attract more customers toward them.
Fifthly, the Company must always maintain all the rules and regulations of the host countries to execute business without any penalty or compensation (deLange, 2016). By maintaining all the rules and regulations, DHL will be capable of maintaining its reputation across the world.
Finally, DHL has to arrange training and development programmes for their employees to enhance their capabilities. It will make them capable of developing the quality of their services because employees will be capable of delivering the best services to the customers. As a result, customers’ gratification will increase enormously, and DHL will be highly profitable.
Conclusion
DHL is one of the leading companies in the courier, express mail and parcel service industry that have operations in most countries of the world. External business environment of DHL has showed that the company enhanced their business by utilizing the available business opportunities of the global market and becoming able to achieve their desired position among their competitors. Knowledge management has played a significant role in ensuring the best use of knowledge within the company and enhancing the employees’ capabilities. DHL has become capable of reducing the different types of expenses through knowledge management, such as employee replacement expenses by increasing employee retention, consultant hiring costs by developing the qualities of employees etcetera. It seems that KM has made them more successful in the industry.
