Contents in this Page
Introduction
Globalization is the extent of interconnectedness and communication among people, global organizations, corporations and governments in which distances are reduced, geographical borders are gradually removed, and the whole world merges (McMichael, 2013). There is a deep relationship between globalization and health. This report evaluates the impact of globalisation on health in poor countries. The report will also demonstrate the dimensions of globalization, the globalization framework and their likely impact on health issues across the countries. How effectively they can address health issues and health inequalities in low-income countries will also be evaluated.
Global Issues: Key dimensions of Globalization and their impact on population health across countries
Globalization has five key dimensions: political, economic, cultural, technological and ecological.
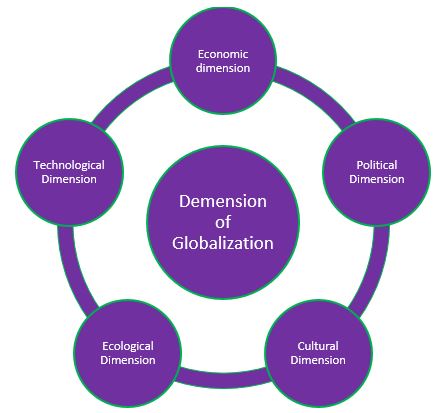
Economic Dimension
The economic dimension of Globalization refers to the extent to which the world economy, world trade, internationalization of business, global corporations, labour migration, and technology migration has happened worldwide and has intensified interconnectedness among the economies and companies (Weisz and Vignola‐Gagne, 2015). Such interconnectedness happens because of foreign trade, foreign direct investment, intensification of the global consumer market etc. Gubler (2011) has revealed that the economic dimension has strengthened the process of the capitalistic approach in which the reaches will be richer, and the poor will be poorer. The validity of this information can be found practically if the statement from Fernando (2014) is critically evaluated. Fernando (2014) has revealed that globalization has resulted in a capitalist world, and such a situation has been intensified by locating the head offices in Western European and North American countries and relocating the production facilities in low-incoming countries such as in South-East Asia or in Africa.
You might also love to read the below post:
How a Mental Health Nurse contributes to Social Care
The economic dimension of Globalization is all about earning and livelihood of people affected, lifestyles, quality of food, and impact on the environment because the economic dimension affects all the above health-related issues (Cockerham and Cockerham, 2014). Economic dimensions and factors greatly affect population health, however, the types of health impact are not the same worldwide. For example, the relocation of production facilities has enabled Vietnam to attract a lot of FDI, which has changed the economic landscape of the country (Ying, Chang and Lee, 2014). Consequently, these have affected the health, lifestyles, and well-being of Vietnamese.
Political Dimension
The political dimension of globalization refers unification of global political powers, countries, continents, and political organizations in which the participants (in an extremely grouped format) share the common goal of their well-being as well as the well-being of the world, sometimes (Sparke and Anguelov, 2012). Group interest of world countries has intensified the process of globalization further through the increase and spreading out of political cooperation around the world. World Trade Organization, World Bank Group, United Nations, European Space Agency (ESA), NATO, World Health Organization (WHO), IMF, UNESCO etc. to name a few only, are some examples of global organizations which were mainly established because of the political dimension of globalization. Some of the above organizations, such as WHO and IMF, work for the whole world, but others, such as ESA, NATO etc., work for specific countries and not for the whole world.
Political relations among countries, globalization and the population’s health worldwide- all these issues are so closely interconnected that they affect the whole world’s health. There are claims from the United States that COVID-19 originated in China, and its outbreak might have deep reasons for political issues (Sahin et al., 2020). Since the outbreak, the world has seen the globalization of a disease: COVID-19 and the death of hundreds of thousands of people.
Technological Dimension
The technological dimension of globalization is one of the factors which affected globalization the most. It refers to the advancement of telecommunication, information technologies, communication, transportation, production, and health systems (Martens et al., 2010). Technological advancement has eased communication from one former of the world to another corner, improved transportation systems, improved health systems and machinery, and improved scientific research.
Technological advancement has critically affected global health. For example, after the outbreak of COVID-19, scientists, research organizations, WHO, and governments are relentlessly working to innovate the vaccine for the disease (Arnout et al., 2020). They are helping the whole world in research by making the data available and interchanging valuable information among themselves. In the meanwhile, the University of Oxford (2020) has reached very close to inventing an effective vaccine, the University has declared that it will make the formula and data open to the whole world for free.
Cultural Dimension
Culture is another important factor which has contributed greatly to strengthening globalization. The cultural dimension of globalization refers to the free flow of cultures worldwide through the use of communication technologies, the free flow of information, the impact of television and new stream such as NETFLIX, and the transformation of culture (Jensen, Arnett and McKenzie, 2011). All the above factors have greatly affected globalization. For example, NETFLIX has enabled any people with an internet connection to see Hollywood movies sitting in the corner of a room in a remote part of the world.
Cultural dimensions and factors also affect the health of a specific country. India is enriched with its own culture, and the people of the country have a habit of following their own culture. However, the free flow of information, culture and communication has invaded the cultural identity of India (Gopalkrishnan, 2018). A large number of people in India now spend a remarkable amount of time on social media, YouTube, NETFLIX etc. All these have been transferred from the western world. Gopalkrishnan (2018) has revealed in his research that the changing landscape of cultural values in India has seriously affected a large population’s psychological health and well-being.
Ecological Dimension
The ecological dimension of globalization refers to environmental protection, population growth, access to health, education and other basic needs, bio-diversity and well-being of the world (Fominaya, 2014). The world’s ecological system is highly affected by the impact of globalization because of increased industrialization resulting from globalization.
The ecological Dimension has significantly affected the health and wellbeing of certain parts of the world. As shown in the earlier example about Vietnam, where a larger number of industries have been established, the region is seriously being polluted by industrialization, and this has a serious negative impact on the mass public health of the country (Ying, Chang and Lee). This example shows how the ecological dimension of globalization affects the health of a country.
Impact of Globalization on Health in poor countries
Among all the issues faced by the health sector, health poly makers and public health practitioners, the impact of globalization is the most on public health of any country (Woodward et al., 2001).

Shows a comprehensive framework indicating how the factors of globalization can have a significant impact on population health. This section has critically evaluated how different countries have benefited in different aptitudes because of globalization. The above framework suggested by Huynen, Martens & Hilderink (2005) has been adopted to evaluate the scenario.
Health Policies and Health Services:
Individual country-wise health policy, health-related policy and health services are generally determined by the economic condition of respective countries and by global institutions such as the UN or WHO (Turner, 2011). Health policies and services are greatly affected by the socio-economic condition and sustainability of the country. As a result, countries do not have the same capability of compiling strong and convenient health service policies. Though globalization has helped countries to strengthen their economic condition, countries have not been able to equally take care of their health system (Labonte, Mohindra and Schrecker, 2011).
| Countries | Year | Fertility Rate |
| Afghanistan | 2018 | 4.5 |
| Chad | 2018 | 5.7 |
| Nigeria | 2018 | 5.4 |
| Denmark | 2018 | 1.8 |
| Canada | 2018 | 1.5 |
| Belgium | 2018 | 1.6 |
| Australia | 2018 | 1.7 |
The above table shows both the least developed nations and developed nations. It can be seen that poor nations demonstrate higher fertility rates which results in more population and further property. On the other hand, developed nations demonstrate less birth rate which means less population.
The above analysis clearly shows that though globalization has an impact on the whole world, developed countries get the best of globalization and poorer nations get the least.
Economic Development & Trade:
Globalization and global economics have a tremendous impact on the economic development of specific countries, regions and on economic zones (Labonte, Mohindra and Schrecker, 2011). The impact is different in various parts of the world. Turner (2011) has revealed that the countries that are already developed and have specific guidelines and policies on economic relations with other countries get a lot of benefits of globalization. However, the author has also revealed that developing and emerging nations gained the most out of globalization.
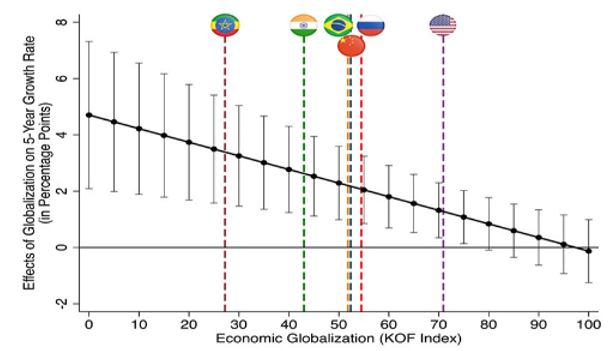
The above graph shows that the mentioned countries such as India, Brazil, China, and Russia are emerging and developing nations. The graph also shows that these emerging nations are the ones that gained the most from Globalization through the utilization of global opportunities. Among the countries, Ethiopia is one of the LDCs, and this country also gained 4-points from globalization.
Knowledge, Social environment and lifestyle:
Knowledge of wellbeing, social environment and lifestyles are also highly affected by globalization (Hu, 2011). In this case, globalization has benefited the rich nations because of their already established education system, social norms and lifestyles.
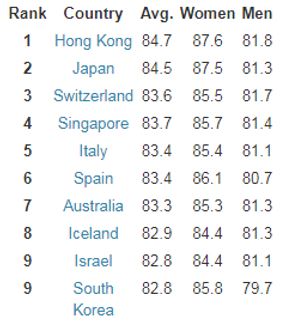
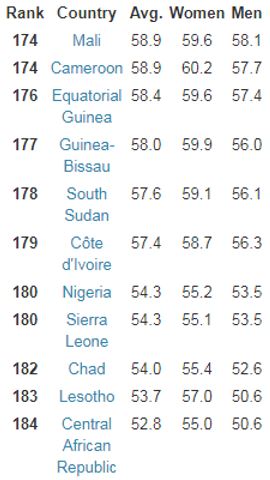
The life expectancy rate shows the expected number of total years a person is expected to live in a country. High expectancy indicates that a country has well control over the health system of the country (Bhatia and Rifkin, 2010). Figure 5 shows the life expectancy in the world’s highest ten countries, with an average expectancy of 83 years. On the other hand, figure 6 shows life expectancy in the world’s least ten countries, with an average expectancy of 56 years. This clearly indicates that Globalization has not increased the lifestyles and well-being among the LDCs though the economic strength has improved.
Physical environment, food and water:
The physical environment, food and water are parts of the ecological system of a country, and they have a significant impact on the health system of a country (Anson et al., 2012). As found in the pervious part, globalization has tremendously modified the relocation of industries. Developed nations have relocated their production sites in emerging LDCs where industries are notoriously polluting the environment (Ofori-Asenso and Garcia, 2016). As a result, they are polluting the physical environment, the food supply chain is polluted, and water is polluted.
WHO (2020) has revealed in their research that LDCs and developing nations will face serious crises of mismanaged urbanization and pollution in all areas; these are likely to have a negative impact on the health of the population living in these countries. OECD has estimated that global chemical production will increase by 85% in 2020 compared to that in 1995, the concern is that one-third of the production will take place in non-OECD countries (WHO, 2020). This implies that manufacturing will take place in developing countries and LDCs. As a result, food, water and the environment will be seriously polluted and damaged.
Part 2: Global Actions-Project-1: UNAIDS
UNICEF established UNAIDS, which project that has been conducted to remove HIV and make people aware of the virus. The project aims to make an AIDS-free generation, especially this project taken to increase awareness of the countries with lower income (Sidibé, Loures, and Samb, 2016).
Global guidelines for UNAIDS initiatives on HIV:
Non-penetrative sex: Non-penetrative sex is also known as outercourse, and it is the sexual activity in which sexual penetration is not included. It excludes vaginal and oral sexual activity and anal; therefore, HIV transferring can be prevented through non-penetrative sex. UNAIDS suggest non-penetrative sex to stop the spreading of HIV (UNAIDS, 2020).
Correct use of condoms: Correct use of condoms for both men and women stops HIV from transferring because condom prevents fluids from entering the body. Therefore, UNAIDS suggest people use condoms in order to stay safe from HIV (Sidibé, Loures, and Samb, 2016).
Pre-exposure prophylaxis: Pre-exposure prophylaxis is the way in which people take medicines to stop getting infected with HIV (CDC: 1, 2020). When people take Pre-exposure prophylaxis, HIV cannot infect the person from sex, injection or drug use. Therefore, UNAIDS recommend people to have Pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Monogamous relations between uninfected partners: Monogamous relation refers to having sex with one partner for life long, and it helps to reduce the risk of HIV (CDC: 2, 2020). For that reason, UNAIDS recommend monogamous relation between uninfected partners.
Antiretroviral therapy: Children can be infected by the mother through breastfeeding during pregnancy and delivery (UNAIDS, 2020). UNAIDS encourage parents to have HIV test in order to prevent the child’s HIV risk by giving antiretroviral therapy to the mother if the parents are HIV positive.
UNAIDS has made a sustainable development goal to prevent HIV within 2030 (UNAIDS, 2020). The actions taken by UNAIDS to prevent HIV are stated below:
Ensuring quality education: UNAIDS ensure quality education for developing and underdeveloped countries about HIV (UNAIDS, 2017). It ensures that HIV-related chapters has been included in schools. As a result, young people will be more responsible in taking health decisions.
Promoting peaceful and inclusive societies: Discrimination, violence, stigma, etcetera factors increase the spreading of HIV among women, children and adults (Jaffee, Shires, and Stroumsa, 2016). UNAIDS encourages governments of less developed countries to conduct rights-based programmes in order to develop the health of the people of the country.
UNAIDS project has become capable of reducing HIV in some countries and has not become capable of reducing it in some countries across the world. In a survey, it is found that 1.7 million people became infected by HIV newly in 2018 (UNAIDS, 2020). The reasons for the increasing number of HIV-infected people are that people do not maintain safe sex rules and other protections that help to prevent HIV. UNAIDS should give more effort to make their project successful so that it can make the world HIV-free.
Project 2: United Nations Millennium Development Goals
United Nations’ project Millennium Development Goals is projected to improve maternal health from malaria, HIV and other diseases (WHO: 1, 2020). The initiatives of the millennium development goals project are:
Strengthen health system: UN works to strengthen the health system by focusing on policies and strategies which are cost-effective (WHO: 2, 2020). It helps the company to implement its project within the targeted budget in countries of lower income.
Monitor and evaluate health: It monitors and evaluates the health of maternal and newborn ill-health (WHO: 2, 2020). Volunteers of the UN work to improve their health, and they become able to develop the health of maternal and newborn ill health in less developed countries.
Sponsoring for investment: UN millennium development goals invest in developing maternal and newborn baby’ health in countries where the financial condition of people are weak (WHO: 2, 2020). By investing in the sector, they can reduce maternal mortality and child mortality.
The millennium development goals of the United Nations have become successful in attaining its targets. It has reduced maternal mortality from 90 to 43 per 1000 lived from 1990 to 2015 (UN, 2015). It refers to the great success of the project. In 1990 the child mortality rate was 12.7 million, which the millennium development project reduced to 6 million in 2015 (UN, 2015). The project ensured the secondary or higher education of the mothers because children of mothers with no education have more mortality rate. Sub-Saharan Africa was the country with the highest child mortality rate, and the millennium development project has reduced the mortality rate of the country successfully.
Comparison: Health inequalities and Effectiveness
Gender inequalities and discrimination have a negative effect on women and girls in society and increase the possibility of getting infected through HIV because they are neglected in less developed countries (Jaffee, Shires, and Stroumsa, 2016). UNAIDS has started gender-transformative HIV programmes to engage men and reduce violence against women (Medlock et al., 2017). It will help the project empower women and ensure better health for them.
On the other hand, the UN Millennium Development Goals project has become successful in empowering women that the UNAIDS project did not. UN millennium development goals project ensures secondary or higher education for women that helps the project to reduce maternal mortality and overcome their weak position in society (McArthur, and Rasmussen, 2017). It seems that the project has overcome the health inequalities successfully and working to prevent them in less developed countries.
It is seen that UN Millennium Development Goals have reduced material death from 90 to 43 per 1000 lived from 1990 to 2015, which refers to the success of the project (UN, 2015). On the other hand, 1.7 million people became infected by HIV newly in 2018 across the world, which shows the project could not achieve its target appropriately, which was reducing HIV from spreading (UNAIDS, 2020). From the data analysed above refers to the success of the UN has become able to attain its target of reducing maternal death and child death but the number of HIV-infected people has increased which means UNAIDS could not attain their goal yet.
Conclusion:
Globalization has a severe positive and negative impacts on the whole world. In terms of economic perspectives, developing and emerging nations have gained the most. On the other hand, they have gained the least in social and environmental indices. The vice versa has happened in the case of developed nations. Several projects have been taken to develop the world’s health condition and maintain equality in the world. There are both positive and negative of globalization on the economy and health issues of low-income countries. UNAIDS has initiated a project to eradicate HIV from the world, emphasizing poorer nations. UN took a project called MDG for poorer and richer nations.
References:
CDC: 1, 2020. PrEP. Retrieved from: https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/prep.html [Assessed on: 30 April, 2020]
CDC: 2, 2020. Monogamy. Retrieved from: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/hivrisk/decreased_risk/communication/monogamy.html [Assessed on: 30 April, 2020]
International Monetary Fund, 2020. World Economic and Financial Surveys. World Economic Outlook Database. Retrieved from: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2018/01/weodata/index.aspx [Assessed on 3 May 2020]
The World Bank Group, 2019. Fertility rate, total (births per woman). Retrieved from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/sp.dyn.tfrt.in?name_desc=false [Assessed on 3 May 2020]
UNAIDS, 2020. HIV and AIDS – Basic facts. Retrieved from: https://www.unaids.org/en/frequently-asked-questions-about-hiv-and-aids [Assessed on: 30 April, 2020]
UN, 2015. GOAL 4: REDUCE CHILD MORTALITY. Retrieved from: https://www.un.org/millenniumgoals/childhealth.shtml [Assessed on: 1 May, 2020]
UNAIDS, 2020. UNAIDS calls for greater urgency as global gains slow and countries show mixed results towards 2020 HIV targets. Retrieved from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/pressreleaseandstatementarchive/2019/july/20190716_PR_UNAIDS_global_report_2019 [Assessed on: 1 May, 2020]
University of Oxford, 2020. Oxford's COVID-19 research receives government funding. Retrieved from: http://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2020-03-24-oxfords-covid-19-research-receives-government-funding# [Assessed on 1 May 2020]
WHO: 1, 2020. Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). Retrieved from: https://www.who.int/topics/millennium_development_goals/about/en/ [Assessed on: 30 April, 2020]
WHO: 2, 2020. MDG 5: improve maternal health. Retrieved from: https://www.who.int/topics/millennium_development_goals/maternal_health/en/ [Assessed on: 1 May, 2020]
World Economic Forum, 2020. This chart shows who gains from globalization. Retrieved from: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/06/chart-of-the-week-distribution-of-globalization-s-gains [Assessed on 3 May 2020]
WHO, 2020. Environment and health in developing countries. Retrieved from: https://www.who.int/heli/risks/ehindevcoun/en/index1.html [Assessed on 3 May 2020]
