Contents in this Page
Introduction:
The Human Resource Strategies of BP will be evaluated in this report, including the HR practices of the company. HRM refers to the management of human resources in an organization to ensure the best use of resources and workforce to achieve corporate and business objectives. This report has mainly three sections. The first section applies High Commitment HRM principles; the second section evaluates the impact of macroeconomic forces on HR strategies, and the final section has analysed how HR of a company deliver HR. It will be tough to cover all the issues in each section; a few issues have been applied in each section to reach sufficient depth. In all the cases, two companies have been used: Marriott International and (British Petroleum) BP. These are well-known companies globally.
You may feel interested to read below blogs:
Functions of Human Resource Management in Sainsbury’s
Practical and Legal Challenges in Employment Relationships
Roles of the Managers and Leaders of Microsoft
Developing Individual Teams and Organizations
Strategic Human Resource Management at Audley
HR policies and practices in BP:
High Commitment HRM (HCHRM)
High Commitment HRM (HCHRM) refers to a set of HR policies which aim at contributing towards organizational efficiency and performance through promoting individual responsibility, employee empowerment, making employees enabled to make individual decision, and emphasizing building systems rather than empowering roles (Boxall, Purcell, 2014). Gould‐Williams (2004) revealed a set of best practices which are practised in HCHRM environment, these best practices are outlined below:
- Employment security and internal labour market (promotions)
- Selective hiring and sophisticated selection
- Extensive training, learning and development
- Employee involvement and participation
- Self-managed teams and team-working
- Higher payment than industry average and performance based payment
- Performance review, appraisal and career development
- Reduction of status and differences
- Work life balance
Above practices of HCHRM clearly imply some features of how a company perceives the employees. Firstly, HCHRM considers that employees are the most important individual asset for the company and they should have the capability to make decisions individually. Secondly, it emphasizes on systems and does not put people in authoritative decision making.
Selective hiring and sophisticated selection is one of the element of HCHRM; it implies that a company should have rigorously-made profiles for candidates most suitable to perform the jobs and that the company should have the right recruitment process in place to ensure that only best-fit employees are selected. Hiring and selection criteria and policies in Marriott International is simplified. Marriott International publishes detailed job advertisement at its website (Marriott International Inc., 2020). However, the site does not inform the selection and recruitment stages; additionally Marriott does not have specialized recruitment and selection programs for individual countries. The company has well more than 7,000 hotels and properties across 131 countries (Marriott International Inc.-2, 2020). This implies that Marriott should have separate recruitment and selection policies for different markets. This also shows that Marriott is far lagging behind using the element Selective hiring and sophisticated selection of HCHRM.
On the other hand, BP has a detailed and rigorously-set policies and approaches of selecting the best-fit employees for individual countries and individual projects (BP plc., 2020). Also, BP has clearly outlined the steps which potential candidates need to pass to reach the final stage of selection (BP plc.-2, 2020). Candidates have to pass approximately 7 to 10 stages (depending on responsibility) to reach final stage of recruitment process. This clearly shows that BP is exerts maximum efforts to ensure HCHRM in the workplace.
Extensive training, learning and development is another element of HCHRM; it implies that a company should have severe and effective training and development programs to enable employees contribute to achieve organizational efficiency (Mello, 2014). VOYAGE is the flagship training and development program of Marriott, it aims to train fresh graduates recruited at the company (Marriott International Inc.-3, 2020). However, it doesn’t expose any other extensive training and development programs for its experienced professionals. Yet, some review sites such as indeed (Indeed, 2020) and Glassdoor (Glassdoor Inc., 2020) revealed a few instances of career progress issues but those severely lack the prospects to be qualified for HCHRM.
In contrast to above, BP truly has an extensive training and development programs for fresh graduates, future leaders and for managers to continue their learning (BP plc.-3, 2020). The company focuses on leadership, communication and presentation skills, and technical capabilities. BP delivers above training through digital learning solutions, BP University, Graduate Challenge Programs, and Future Leaders Programs.
Above analysis clearly demonstrates that in both contents of HCHRM, BP is much close to be a truly HCHRM; in contrast Marriott is far lagging to ensure HCHRM. Bratton and Gold (2012) argued that following the practices of HCHRM is difficult for labour intensive industries such as hospitality; while high-tech companies such as pharmaceuticals, oil extraction companies find it efficient to follow HCHRM. In above analysis, the same has been found. Marriott has more than 174,000 employees, while BP has only around 73,000 employees. Marriott finds it difficult to train and develop such huge workforce; whilst extensive training and development program is mandatory for BP because of the nature of the industry it operates in.
External forces and their impact on HR strategic decision making in BP
External forces are the elements of macroeconomic environmental factors that have severe impact on a business and that a company has no control over (Wright & McMahan, 2011). An organization should not try to control those external forces, rather the company should adopt the HR policies and business strategies to match with those of external forces. Marchington and Wilkinson (2012) revealed that external factors affecting HR policies and strategies include technological environment, economic environment, legal factors, and social factors.
- Technological (advanced technologies, IT learning platforms)
- Economic (COVID-19 and its impact)
- Political and Legal (minimum salary, child labour)
- Social environment (salary vs. work life balance)
Impact of technological factors on HR: Gratton, Hailey, & Stiles (2011) argued that technological factors such as advanced technologies, IT enabled learning and development platforms played the most potential role to influence HR strategies in a company. Technological factors have severe impact on both Marriott and BP; the impact is much more prominent in Marriott than in BP because of adopting highly advanced technologies in hotels by Marriott. Marriott has been immensely affected by advanced technologies and it has already implemented mobile check-in instead of conventional check-ins by employees; rooms have gone keyless, instead face scanners have been enabled; services such as request for an extra towel, coffee, managing room temperature and lighting have all gone under single mobile application which can be operated laying on the bed (Marriott International Inc.-4, 2020). Adoption of such technologies have huge impact on how HR at Marriott compile their human resource strategies. For example HR at Marriott needs to compile their job design to recruit tech-savvy candidate to accommodate the technology powered environment. All these happened because technological development has been widespread in other industries; thus key players in the hospitality industry (such as Marriott, Premier Inn., Hilton Hotel, and Continental Inc.) have also started adopting advanced technologies. Though these technologies cost the companies; but the return is much more rewarding than the investment (Cole & Barker, 2009).
Technology also has huge impact on how BP compiles their HR strategies. Development of web based application, mobile application, motion graphics, and huge adoption of internet technologies have motivated BP HR to design online based learning and development strategies (BP plc.-3, 2020). This company introduced BP learning solutions and BP University which are web based learning platforms which all qualified employees of BP can access from 78 countries of BP’s operation across the world. This has made the company more advanced in promoting learning and development.
Impact of Economic factors on HR: COVID-19 and its consequences have negatively affected businesses globally, Marriott is also affected. Marriott has experienced decline in revenue since the start of the Pandemic. HR of Marriott needed to furlough thousands of employees in March; moreover the company decided to lay off 600 of its employees from the corporate office because of decline of room occupancy and revenue (Murphy, 2020). The impact of economic forces is far more dangerous in case of BP which was forced to cut 10,000 jobs (BBC, 2020). This happened because HR needs to respond to corporate objectives.
Impact of social environment on HR: Social environmental factors such as culture, shared beliefs, perceptions are determined by social and cultural environment (Lengnick-Hall, Beck, & Lengnick-Hall, 2011). Socio-cultural environment forms the perception towards money versus work-life balance. World Economic Forum (2017) reported that Denmark has the best work-life balance in the world. InterNations (2020) revealed that Denmark, Bahrain, Norway, New Zealand, Sweden, The Czech Republic, Costa Rica have best work-life balance in the world. In contrast, countries such as the USA, Australia, Canada, and most Asian countries have more priority for money rather than work-life balance. HR of both BP and Marriott needs to respect these forces and act accordingly. Marriott needs to emphasize on work-life balance features such as earned-leave, vacations, 5-day week in countries such as Denmark or New Zealand. BP has huge operations in oil extractions in Bahrain and Oman where work-life balance is more prevalent than money. Thus BP’s HR emphasizes more on work-life balance features in these countries.
Both BP and Marriott also need to comply with respective national laws related to child labour, minimum payment, and laws on environment pollutions while running operations in respective countries. HR of both companies need to study laws of respective countries and need to act accordingly.
The organization of HR functions and delivery of HR policies
Jackson, Schuler, & Jiang (2014) revealed that HR policies and functions should comply with corporate and business strategies. This implies that HR policies should be adopted with corporate and business level strategies. Ulrich (1996) suggested a model called Ulrich Model of HR policies which was widely appreciated and used in largest organizations to deliver their HR policies and processes.
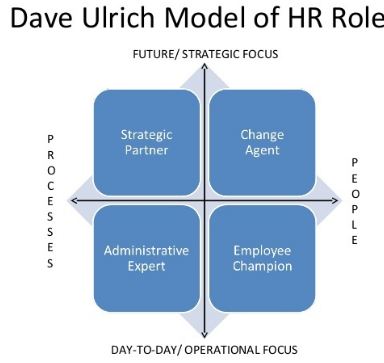
The diagram in figure 1 shows that HR policies have been divided in four orientations: future and process oriented (strategic partners); future and people oriented (change agent); operation and process oriented (admin expert); and operation and people oriented (employee champion). Boselie (2010) revealed that Ulrich Model of HR is generally used in large organizations. The elements of the model are reflected in the HR strategic formulation, process and policy compilation of Marriott and BP.
Future and process oriented (strategic partners): HR strategic partners are the point of communication between internal customers (such as employees, shareholders) and the human resource department of an organization (Huselid & Becker, 2011). Strategic HR partners at Marriott identifies top talents among employees, assess job risks at the workplace, help to fill in job vacancies, and share HR goals with employees. The most critical challenge these HR strategic partners face is when the core business units do not share their corporate and business strategies with them. As a result they cannot share the same with internal customers. To avoid such situation, employees at Marriott should be transparent in communication and information sharing.
Future and people oriented (change agent): This is the portion of the HR team who shares the changed objectives and goals to all the members of the organization (CHUANG & Liao, 2010). People in training and development section of the HR team at Marriott and BP play the role of change agents in respective organization. Now making lessons and programs deliverables online is a complex job and require extensive capability and skills. Thus, they faces obstacles to make all employees capable to assess and get benefits of the programs.
Operation and process oriented (admin expert): This group of employees takes care of jobs related to administration such as changes in laws and legislation, handling legal cases with external parties, complying with health and safety measures, compliance with environmental laws etc. (Marler & Fisher, 2013). This groups is also common both in BP and in Marriott. HR professionals in Admin team at Marriott supervises if the hotels are complying the environmental laws, child labour laws, and minimum salary legislations etc.
Operation and people oriented (employee champion): These group of HR team executes general HR activities such as taking care of employees satisfaction level and then makes strategic HR plans to make them engaged and satisfied (Lengnick-Hall, Lengnick-Hall, & Rigsbee, 2013). General HR teams at Marriott plays the role of employee champion. It helps Marriott to understand the perceptions of employees towards the company and can utilize the information to optimize HR strategies.
The benefit that HR of Marriott receives from Ulrich Model of HR policies is that it implements role based HR policies rather than designation based HR. It enables the company to build system and streamline the HR execution.
Conclusion
High Commitment HRM is strongly associated with organizational efficiency and productivity because HCHRM strongly emphasizes on building efficient systems rather than emphasizing on individual power. However, it has also been found that HCHRM is more suitable in tech-savvy organizations, such as pharmaceuticals industry, and less applicable in labour based organizations, such as hospitality industry. External forces such as economic environment, political forces, and social factors have severe impact on how HR makes its policies. HR policies must be compiled considering these issues. It has also been found that Ulrich Model of HR helps an organization to focus on specific HR functions and helps the organization to streamline the HR functions.
References
BP plc.-2, (2020). The application process at BP. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/careers/careers-bp-candidate-support-application-process.pdf [Assessed on 2 October 2020]
BP plc.-3, (2020). Learning and development. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/careers/life-at-bp/learning-and-development.html [Assessed on 2 October 2020]
BBC (2020). BP to cut 10,000 jobs as virus hits demand for oil. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.bbc.com/news/explainers-52966609 [Assessed on 3 October 2020]
Bratton, J., Gold, J., (2012), Human Resource Management: theory and practice, 5th edition, Hampshire: Palgrave MacMillian
Glassdoor Inc., (2020). Marriott International Review [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.glassdoor.com/Reviews/Marriott-International-Reviews-E7790.htm [Assessed on 2 October 2020]
InterNations (2020). Top 10 Countries with a Great Work-Life Balance. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.internations.org/magazine/top-10-countries-with-a-great-work-life-balance-39439 [Assessed on 3 October 2020]
Marriott International Inc., (2020). Corporate Careers. [Online] Retrieved from: https://careers.marriott.com/career-paths/corporate/ [Assessed on 1 October 2020]
Marriott International Inc.-2, (2020). We are Marriott International. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.marriott.com/marriott/aboutmarriott.mi#:~:text=Offering%20the%20most%20powerful%20portfolio,experience%20and%20expand%20their%20world. [Assessed on 1 October 2020]
Marriott International Inc.-3, (2020). Opportunities for Post Graduates. [Online] Retrieved from: https://university.marriott.com/post-graduates/ [Assessed on 2 October 2020]
Indeed (2020). Marriott International. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.indeed.com/cmp/Marriott-International,-Inc./reviews?ftopic=jobsecadv [Assessed on 2 October 2020]
Marriott International Inc.-4, (2020). Hotel Technology. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.marriott.com/meeting-event-hotels/meetings/mobility-and-tech.mi [Assessed on 2 October 2020]
Murphy, C. (2020). Marriott to lay off hundreds of workers at Bethesda headquarters due to travel decline. USA Today. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2020/09/08/marriott-lay-off-hundreds-workers-due-covid-19-travel-decline/5743857002/ [Assessed on 3 October 2020]
Mettl, (2020). Managing HR Roles: David Ulrich’s HR Model. [Online] Retrieved from: https://blog.mettl.com/managing-hr-roles-david-ulrich-model/ [Assessed on 3 October 2020]
Mello, J. A. (2014). Strategic human resource management. Nelson Education.
World Economic Forum (2017). Denmark has the best work-life balance. Here’s why. [Online] Retrieved from: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/03/denmark-best-work-life-balance-oecd/#:~:text=According%20to%20the%20OECD%20Better,the%20OECD%20average%20of%2013%25. [Assessed on 3 October 2020]
