Internal Environment Analysis of Toyota will be conducted in this report. SWOT analysis and BCG matrix of the company will be analysed to show the internal capabilities of the company. Competitive analysis has also been conducted by applying Porter’s five forces model on Toyota.
You may also feel interested to read the blogs:
Unique Selling Point of Toyota
External Environment Analysis of Toyota
Risk Management at British Airways
PESTEL, SWOT and Porter’s Five Forces Model of MC Donald’s
Contents in this Page
SWOT Analysis of Toyota:
Strengths, Weakness, Opportunities and Threats of Toyota has been presented below:
| Strengths * Toyota has created strong brand value across the world, which helps them to maintain continuous sales. * It has 20 R&D centres and invests a huge amount in the R&D sector therefore, they become able to produce the latest cars (Toyota Europe, 2020). * Global supply chain of Toyota helps to minimize market-based risks. | Weakness * Hierarchical organizational structure of Toyota prevents maximum resilience from regional operations. * The company greatly depends on North American and Japanese markets, but they should focus more on other countries like as Japan and North America (Matsuo, 2015). * Secret culture of the company reduces the response time of the rising programs of the company. |
| Opportunities * Emerging markets of developing countries have the potential to make Toyota more profitable. * Demand for fuel-efficient automobiles is increasing, and Toyota may take this opportunity as a turning point by inventing fuel-efficient cars. * Weakness of Yen to USD is the higher competitiveness of Toyota cars which are exported from Japan to the US (Yamashita et al., 2015). | Threats * Competitors of Toyota are producing automobiles at lower cost and are capable of delivering the automobiles at a lower price (Eichelberger, and McCartt, 2016). Therefore, customers switch to lower-priced cars. * Increasing the price of fuel is increasing the costs of Toyota, which reduces the profit level. * Competitors such as Honda, Ford and GM are producing innovative automobiles, which is a great threat to Toyota. |
BCG Matrix of Toyota:
The competitive advantages of business units are analysed through the BCG matrix. This analysis will show Toyota which products they should focus more and should not focus on. BCG matrix of Toyota has been evaluated below:
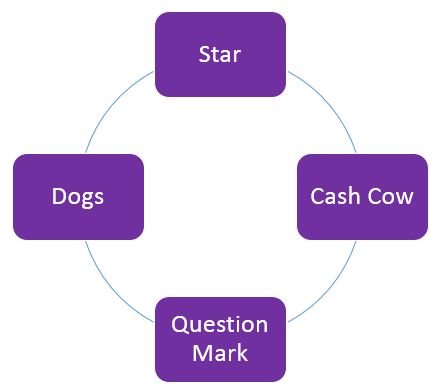
Star: Financial services strategic business unit of Toyota falls in the category of stars. The company earn high profit from the sector, and it has the potential to bring more profit in future (Coetzee et al., 2016). The brand strategic business unit of Toyota also falls in this category. The company attains 20% of its market share from this business and is forecasted to increase the profit of this sector by about 5 % within the coming years (Chiarini, and Vagnoni, 2015). It indicates the growth rate will remain high in this sector. Toyota should increase their sales of this service through market penetration therefore, customers of untapped areas will get the service, and it will bring more profit.
Cash Cow: Supplier management service strategic business falls in the cash cow category of the BCG matrix (Dillon, 2019). The company have generated a specific amount of revenue from this service, but the market is declining. Therefore, Toyota should stop investing in this sector but operate it to attain profit as long as possible without new investment. Number 3 brand strategic business unit also falls in this category. The market share of this sector is also falling in past years, but this sector has the potential to attain more market share. The company should invest in R&D to grow in this category and earn profit.
Question Mark: Local food strategic business is the product of question marks in the BCG matrix of Toyota (Coetzee et al., 2016). Customers are becoming weaker to local foods. Therefore, this sector refers high growth rate for the company. Toyota should invest in this sector to achieve high growth and become profitable. The confectionary strategic business unit also falls in a question mark. This sector has a slow growth rate but can increase growth by investing in it.
Dogs: The dog category product of Toyota is the plastic bags business unit which they have been facing loss for some years (Toivonen, 2015). Because of increasing awareness toward saving the global environment the market is declining. Therefore, the company should stop investing in this product. Synthetic fibre products also belong to the dos category and the market is falling. They should not invest in this product anymore to avoid more loss.
Competitive Analysis of Toyota
Porter’s Five Forces Model of Toyota
Porter’s five forces model has been applied to Toyota to analyse the competitive position of the company.
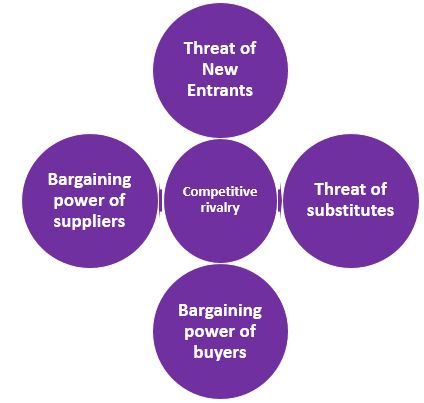
The threat of new entrants: Low: Barriers of this industry will not permit new entrants to enter in the sector easily, and it needs huge capital. Therefore, new companies are unable to invest a huge amount of capital. Even the global presence and brand value of Toyota are impossible to replace for new companies (Frisch et al., 2016).
The threat of substitutes: Medium: There are some substitutes for Toyota products that customers can switch to. Switching costs for cars are less than Toyota. Therefore, the risk is medium for the company. But the company have started producing cars which are fuel efficient in order to reduce customers’ cost and hold them (Yoshida, and Kojima, 2015).
Bargaining power of buyers: High: The bargaining power of customers is high for Toyota (Matsuo et al., 2016). Because of the lower switching costs of other companies, customers can switch to other companies’ services. Customers choose a suitable option for themselves. To maintain customers’ demand, Toyota delivers the latest cars which helps them to maintain its customer base.
Bargaining power of suppliers: Low: The bargaining power of suppliers in front of Toyota is weak (Kojima, and Fukazawa, 2015). It has a large number of suppliers globally and, therefore can manage mechanisms from anyone of them. Toyota is a world brand. Therefore, suppliers get benefited from the company, which is another reason for its weakness.
Competitive rivalry: High: Ford, Volkswagen, Suzuki, Nissan, Honda, General Motors, BMW & Mercedes are the key competitors of Toyota (Notesmatic, 2019). All of these companies are investing more in R&D and focusing on customers’ convenience. Therefore, Toyota faces high competition in the industry.
Reference
Toyota Europe, 2020. Toyota in the world. Retrieved from: https://www.toyota-europe.com/world-of-toyota/this-is-toyota/toyota-in-the-world. [Assessed on: 1 March 2020]
Toyota Global, 2014. Annual Report of Toyota 2014. Retrieved from: https://www.toyota-global.com/pages/contents/investors/ir_library/annual/pdf/2014/ar14_e.pdf. [Assessed on: 2 March 2020]
Toyota Motor Corporation, 2020. Toyota Environmental Challenge 2050. Retrieved from: https://global.toyota/en/sustainability/esg/challenge2050/. [Assessed on: 3 March 2020]
Tomiyama, E., 2014. A Study of Semi Knock Down (SKD) Production and Sales and Marketing Strategy in the Russian Far East. The ortheast sian conomic eview.
