Contents in this Page
Introduction
Organizational behaviour is the attitude of humans toward their organization and it is the behaviour by which people interrelate with groups. This article is about organizational behaviour models on Dr Martens which is a footwear industry. Organizational behaviour is a very important issue because it exposes the reasons behind people’s behaviour in their organization. It helps to identify the causes and effects of behavior and how employees influence their organization. It also indicates how employees affect each other; furthermore organization affects employees and encourages them. In this report, the influence of organizational culture, politics and power have been evaluated.
The impact of culture, politics and power on employees’ behaviour
The organizational culture at Dr. Martens: Handy’s Model of Culture
Organizational culture is the values and behaviours that influence the spiritual environment of an organization (Dinh et al., 2014). It impacts the way employees and members of an organization cooperate and with the stakeholders of a company.
At Dr. Martens, it is believed that organizational values are highly personal to the organization and it is unfair to lead an organization with about thousands of employees with an organization’s personal value. Therefore, leaders at Dr. Martens believe that employees should be led by their own values. As a result, employees can perform their best when they are given the chance to exhibit their own passion, own color. The company also recognizes that it should have a set of principles and behaviors that should be determined with the participation of large number of employees.
Application of Charles Handy’s cultural model in Dr. Marten
According to philosopher Charles Handy’s cultural model, there are four types of culture that companies follow such as: power, task culture, person culture and role culture (Avolio and Yammarino, 2013).
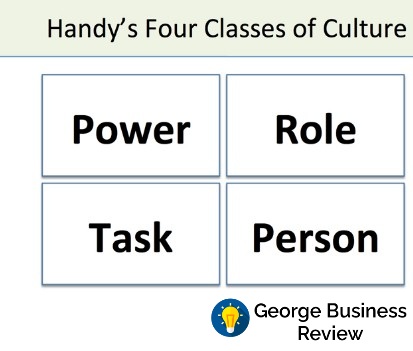
Firstly, Power is that organizational culture in which only few people have the power of taking all decisions, have hierarchical bureaucracy (Van. 2013). This is not a democratic process and opposed to the practices done in Dr. Martens where democratic decision making process is practiced.
Secondly, in the task culture, individuals of common interests make team to achieve their target or prevent problems from the organization (Chemers, 2014). It has no single source of pwer, follows matrix organization. This culture has very much similar to those practiced in Dr. Martens.
Thirdly, person is the organizational culture in which employees feel themselves most powerful, they similar types of skills (such as accountancy of lawyers). This also does not match with those of Dr. Martens because employees have diversified types of skills and expertise.
Finally, Role is the culture where an organization distributes the roles and responsibilities of employees by considering their educational qualification, concentration and engagement. Here, power derives from positions, expert power has no power. This character does not match with culture practices followed at Dr. Martens.
After analyzing Handy’s cultural model it seems that, Dr. Martens follows a specific features of both Task culture the Role culture. As per the model, this is a hybrid cultural model. Here, the divisional managers, regionals heads are delegated with authoritative and decision making power at their ends; this matches with Role culture. Dr. Martens also has hierarchical bureaucracy and position power; these features can be observed in Role culture. However, Role culture assumes that expert has no power; this is opposite to the cultural philosophy of Dr. Martens. Dr. Martens form different matrix teams to solve specific problems this go with Task culture.
You might also be interested in: Definition of human resource management Tips to make a workplace effective How HRM contributes to high performance working? Strategic Management of Human Resources
How beliefs and behaviors have affected Dr. Martens
Dr. Martens have compiled a set of behavior and policies to be followed by all employees in very hierarchy. How these helped Dr. Martens to turn around the business is analyzed below:
Creativity and passion of Martens help them to bring new products, new services, new marketing strategy and new distribution channel. They explore their products and become able to increase their customers. Passionate attitude motivates creative employees to work consistently unless flawless results are achieved, turning the business to growth.
Their fearless attitude helps them to take new challenges and encourage them to achieve success in the foot ware industry.
Resilience helps them to stay strong and maintain their efforts. Rebellious indicates that they provide service in different way such as: they produces shoes by maintaining the tradition of shoes of 1970 and 1980. It makes their boots and shoes different from the competitors which attracts more customers for Martens.
Integrity and professionalism among employees make them loyal yet strict to the norms and culture. This helps Dr. Martens to keep up with the long practiced heritage in boots.
Influences of power and political behaviours
Martens uses different type of power while taking important decisions. How power influences the teams and individuals of Martens has been described below:
Power behavior at Dr. Martens: Application of French and Raven’s 5 forms of power
French and Raven conducted a power research and revealed five forms of power such as: reward power, expert power, legitimate power, corrective power and referent power (Pakdel, 2013). These are analyzed below:
Reward Power have motivated employees: Martens offer reward to have best performance from employees and it inspires employees highly. Monetary rewards and rewards of state of art working environment have motivated employees to relocate to new workplace. Moreover, employees have been rewarded with independence of decision making which is assumed to be the biggest reward. This concepts relate to the theory of Power by French and Raven who revealed that Reward is that power which is used to inspire employees to increase employee engagement (Elliot and Dweck, 2013).
Expert power have created ecology of sustainable learning: At Dr. Martens, when an employee works in a group and has more knowledge than others, he will get the position of authority. Expert power has brought better result for Martens because group members are able to increase their knowledge by following their authority. This creates a sense of sustainable learning. This knowledge is in line with the same theory in which it is said that expert power achieved on basis of one’s expertise on his knowledge and experience (Weiner, 2013).
Legitimate power: Legitimate power is the power someone gets with their joining to specific position. For example, president of Martens have the power to take significant decisions. Their decision influences all and employees have to obey their decision. One limitation is that if president takes any wrong decision, employees have to obey their decision without protesting.
Coercive power is not good at all levels: This type of power makes the team leader at Martens more powerful and they control other employees. Sometimes the persons who have coercive power can misuse it and it will create problem for Martens.
Referent power: The persons who are able to influence people positively with their charm, good looks and attitude get the power (Matos et al., 2014). Need for referent power will inspire employees to give their best in Martens to get the chance to lead. But anyone can achieve the power by creating their appeal, therefore experience are ignored in this power.
Political behaviors:
How political behaviors influences Martens is given below.
These are related to Chanlat’s political theories.
Political Participation is widely practiced at Dr. Martens: Political participation is the process of individuals in participating democratic decision making (Doppelt, 2017). Martens applies the process of political workshop with participation. For example, Martens arranged a workshop with marketing partner and 78 employees got the chance to participate. The employees expressed their opinion about what is good in Martens, what type of change should bring and created a framework. These framework helped them to make their service more innovative, position strong and make their services different from competitors. This also helped the company to make the relocations and restructure process more smooth.
Freedom of choice: Freedom of choice means employees get the chance to do their work independently (Goetsch and Davis, 2014). Martens gives their employees opportunities to work with their choice. They do not try to compel employees to follow Martens value. The company understand that employees have their own choice. It makes their employees more committed and loyal toward their company and Martens get best output from employees.
Decentralization of power: Decentralization took place in Martens at the time of expansion. The company gave all the responsibilities to the regional directors when it expanded their business. It helped the directors to handle their business independently and appointed skilled employees for the business. All employees got equal facilities from Martens and it made the company more successful.
Motivational theories helped Dr. Martens during restructuring and relocation process
During 2010 and 2013 when the company took major initiatives of relocation and restricting the company culture, it took some important steps related to culture and these steps helped Dr. Martens to make a sustainable way of conducting business. The number of employees have increased to almost 1300 from 500, the number of outlets increased, sales revenue increased tremendously (case study & New York Times, 2012). All these happened because employees were motivated and they exerted higher level of efforts. The strategies that motivated employees have certain connections with different motivational theories. These are explored below.
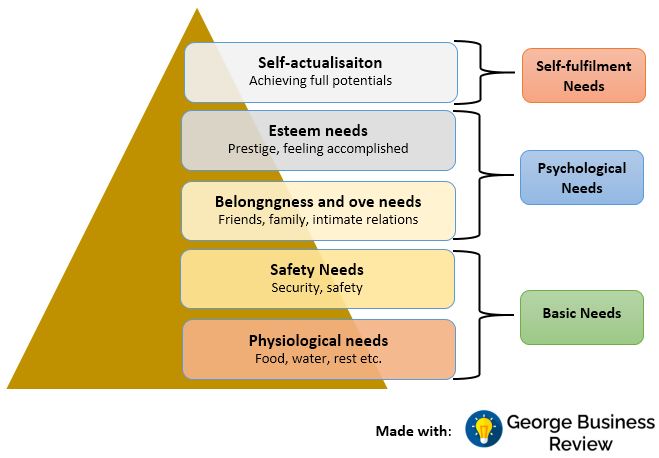
Emphasis on passion and individuality of employees: related to self-esteem needs of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: The case study and relevant sources have revealed that Dr. Martens did not imposed organizational values, which is perceived as very much personal to the organization, on the employees. Rather, the company believes that employees should be led by their own values, passion and integrity. Miner (2015) reviled that self-esteem stage of Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs is the highest stage of people’s need. By emphasizing on passion and individuality of employees, Dr. Martens have ensured the highest level of people’s needs. Such higher level of need satisfaction had significant impact on the company while it was restructuring the relocating the offices and activities by motivating the employees to work at their best.
A set of behavioral framework and its circulation has formed organization culture ensuring cogent growth and restructure: Related to goal-Setting Theory: To make a unified efforts and initiative, Dr. Martens has made a set of behavior and attitude with a contribution of all major employees of the company. Later on, Dr. Martens circulated the set of behaviors in all hierarchies of the company. Dweck (2013) have found that Goal-Setting theory also work in the same way by making a set of unified goals which all the employees should follow. Such commonly followed goals ensure cogent growth and firm structure. During the restructuring and relocating the organization, such goals were highly important because it created a system of working helping Dr. Martens to achieve the ultimate goals of expansion and positive growth.
Empowerment of regional offices paves the way of strengthened structure and culture: Related to Expectancy theory of Motivation: During the expansion of Dr. Martens and relocation of production activities in third world countries and design and head office to London; the regional offices were given the right and power to take their own decision (Case study). This makes a link to the Expectancy theory of Motivation which has been explained by Firestone (2014). The author revealed that employees exert higher level of efforts with a hope to gain good rewards. At Dr. Martens, employees were given high rewards: independence to run their regions. Such motives highly motivated the employees to do their best during relocation.
Generalized system of HR motivates employees in all regions: Related to Equity theory of Motivation: The case of Dr. Martens have shown that employees in all regions were treated in the same way regardless of the number of employees or their location. Equity theory of Motivation explains that employees work their best when they get fair treatment (Graham and Weiner, 2012). Such fair treatment created positive impact on employees by making them feel valued which later on must have motivated them. High motivation and valued attitude have ensured cogent growth and expansion.
Effective Team development in Dr. Martens
Dyer and Dyer (2013) have explored that individuals and teams should be engaged with specific roles and responsibilities because such roles keep them focused and engaged to achieve the team objectives. In teams, it happens quite often where team members have conflicting roles and responsibilities and they compete with each other rather than supplement each other. To avoid such repetition, Belbin’s Team Roles theory can be applied. Dr. Martens is a growing company with about 1500 employees. In below discussion, how Dr. Martens can make effective teams has been analyzed.
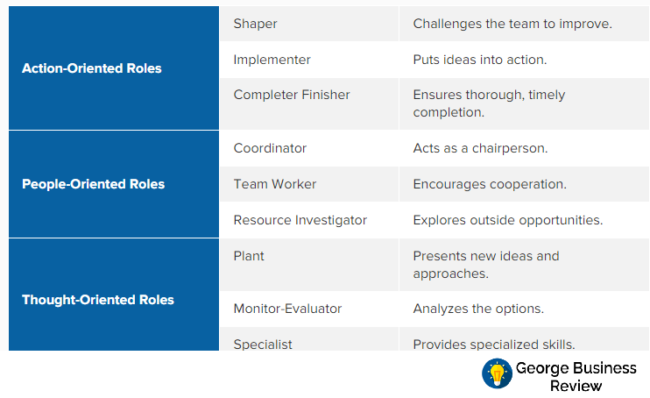
Action oriented roles at Dr. Martens:
Dr. Martens should have Sharper: Sharpers are challengers, dynamic and extrovert who question the current status (Ricca et al., 2012). These people will make new ideas and concepts and will effort to change the obstacles and thus will play significant role at Dr. Martens. They will play the role of leaders and they will move the company.
Dr. Martens should have Implementer supported by Complete-finishers: Implementers are opposite to sharpers; ensuring implementers will supplement each other and will really make a high performing team (Strnadova et al., 2014). Implements perform the jobs, they are introvert in nature.
If Dr. Martens only have sharpers, they will compete with each other and no job will be performed correctly due to lack of implementer. At the same time, implementers should be supported by Complete-finishers who will find faults and recommend better ways of completing the task. Combination of Sharpers and implementers will make an effective combination of teamwork at Dr. Martens: one group will generate idea and other group will implement.
People oriented roles at Dr. Martens
Coordinators will play vital roles: coordinators are generally leaders, they make the objectives and goals (Fapohunda, 2013). Regional managers at Dr. Martens play the role of coordinators. They should not work at root labels; rather they should make strategic directions and subordinates should implement the goals.
Team workers will cooperate among members: Team workers work below coordinators; they make sure that employees in the team are working to achieve the set goals (Hurst et al., 2015). This will play important role at Dr. Martens because team workers will play the role of facilitators. There are large number of employees and teams at Martens, they will create complexities and conflicts among themselves. Team workers will solve the complexities through effective negotiations.
Resource Investigators will find new opportunities: These groups will look for new opportunities, new contracts and new relations (Riener and Wiederhold, 2012). As a fashion company, Dr. Martens need a large number of manufacturers, marketers, agencies, subcontractors etc. Resource investigators will investigate the new contacts and relationship.
Above three categories have maintained a hierarchy: each group will supplement other rather than competing with each other. This will ensure efficient work flow and implementation of orders at Dr. Martens.
Thought Oriented Roles at Dr. Martens
There should be creative people at Dr. Martens: Creative people are called Plants who work with creative ideas and ways of getting the work done (Miller, 2015). Being a fashion and trendy company, such people play significant role to research and find new products, find new process of production, analyze and set the new trends at Dr. Martens. Their creative ideas and process will help the company stand out from crowd.
Monitor-Evaluator can fine tune the creative ideas: The plants have some limitations: such as often their ideas are not feasible. Thus, monitor-evaluators are those people who evaluates the suggestions of the plants (Johansson, Skantze and Gustafson, 2013). Monitor-evaluators will find the limitations, obstacles, commercial viability and opportunities; as a result they can add significant value to Dr. Martens growth and prospects.
Specialists will get the job done: Specialist are those people who will do the jobs, they are the main source of growth for any company. Dr. Martens is a boot and fashion cloth manufacturer, it needs to do production in many countries, and thus specialists play significant roles to achieve the objectives of the company.
On above three categories, no one compete with each other, rather they help each other to achieve the objectives of the company. By thus, Dr. Martens will make an effective team.
Leadership at Dr. Martens
Path-Goal theory of Leadership
Path-Goal theory of leadership is based on the concept in which leadership is not perceived as a source of power, rather leaders work as a coach and coordinator to navigate the employees by showing them the obstacles that they may face to achieve the objectives (Northouse, 2018). This theory considers and number of issues and based on all of them, leaders select one specific leadership style for certain group of employees.
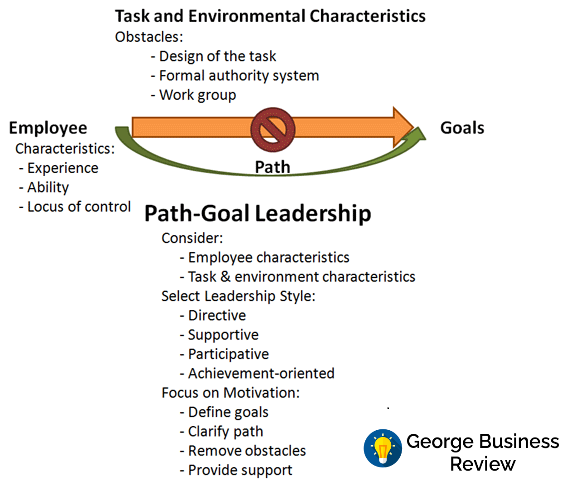
This leadership style has a number of leadership options, based on circumstances, leaders follow specific style. The leadership style followed at Dr. Martens adopted the path-goal leadership styles.
Dr. Martens follow directive leadership styles with workers: The Company believes that some employees need directive leadership, implementers are generally those types of people. This group of employees generally require directive leadership style (Antonakis and House, 2013). Managers and leaders in Martens apply directive leadership to lead workers and people who are implementers.
Dr. Martens follow supportive leadership with potential and talented people: Based on needs, well-being of the employees, managers at Dr. Martens apply supportive leadership styles. People with passion, talent and generally senior level employees are treated with supportive leadership. For example, in case of relocation in foreign countries, employees at foreign countries are treated with all necessary supports. Even they were treated at the same way as the domestic employees. This implies that managers at Dr. Martens support their certain employees.
Participative leadership is also followed: This is another dimension of leadership suggested by path-goal theory of leadership which means employees get the chance to participate in the leadership and work process (Lussier and Achua, 2015). At Dr. Martens, employees can share information and get information through an internal newspaper and communication channel. It enables the employees to take part in the leadership style.
Challenge orientation: This is a leadership style in which employees are challenged with new goals and targets (Parris and Peachey, 2013). Designers and marketing and sales people are challenged by the managers to bring new designs for designers and to increase sales for sales people and to make innovative marketing campaigns for marketing people. The goals are highly ambitious which employees work to attain.
Bas on the analysis above, all the dimensions of leadership styles of Path-goal leadership theory are followed at Dr. Martens. Therefore, the theory is completely adopted at Dr. Martens.
Change management at Dr. Martens
Frankland et al., (2013) have revealed that the world has been undergoing through rapid change, an organization should also be adapted to change quickly. In the rapidly changing world, companies that can adapt to change can sustain and rapidly grow; whilst companies that cannot accept change fall behind the competition and after a few while they become diminished (Hayes, 2018). Change management is a complex process which should not be rapid, it should be slow but consistent. A number of changes took place at Dr. Martens and employees accepted the change without any obstacles. In this section, how employees accepted changes will be evaluated with the application of a change management theory called Lewin’s Change Management Model. This model implies that change should happen following three steps: Unfreeze, change, and refreeze (Cameron and Green, 2015).

Unfreezing the activities: Unfreezing is the first segment of Lewin’s change management model. In this segment an organization prepares their employees for the change they are going to face (Doppelt, 2017). The company shows their employees that the existing way of operating cannot be continued. A company convinces their employees to adopt with the changes of the future which will be taken for the betterment of their company (Goetsch, and Davis, 2014). Martens conduced a meeting with one of their marketing partners and had 78 employees in the meeting.
The employees helped the company to make the effective framework defining their beliefs and behaviors. Martens informed all the employees about their employees and had the scope to preparing their mind. The settled new sets of rules and policies and informed the employees therefore the employees did not protested against Martens. The employees knew about the relocation and were ready to move with their company. To decrease the production cost they decided to outsource from China, India and Thailand which was also accepted by the employees.
Making the changes: In the segment after unfreezing the activities, an organization begin their reformation (Matos Marques Simoes, and Esposito, 2014). Martens shifted their business from Northampton to London which was the biggest change of the company. Which brought profit to the company by making their expansion successful. At first there was not enough place for all employees therefore they shifted slowly. Main factory of Martens also had been shifted to London. They started to outsourcing from China, Thailand and India which reduced their production cost and brought more profit than before.
Refreeze: After unfreezing activities and making the changes, refreeze conducts (Pardo-del-Val, Martinez-Fuentes, and Roig-Dobón, 2012). It helps employees and a company institutionalize the changes. Martens made sure that the changes are used properly and it brought better outcome for them. The company had utilized the changes appropriately and got highly benefited. The decision of expanding business through shifting London was the best decision and Martens has become more famous than before. Outsourcing has reduced the production cost and it increased the profit level highly. They can produce more shoes within low cost which helps them to fulfill the increasing demand of customers.
Conclusion
Martens has go through with so many changes and their employees were adaptive with all the changes. They never compelled employees to accept the value of the company even let them do their staffs according to their plan. They have been treating their all employees with equal priority which increases employee retention therefore they are becoming more successful by ensuring employees retention.
References
Avolio, B.J. and Yammarino, F.J. eds., 2013. Transformational and charismatic leadership: The road ahead. Emerald Group Publishing.
Dweck, C.S., 2013. Self-theories: Their role in motivation, personality, and development. Psychology press.
Dörnyei, Z. and Ushioda, E., 2013. Teaching and researching: Motivation. Routledge.
Doppelt, B., 2017. Leading change toward sustainability: A change-management guide for business, government and civil society. Routledge.
Dyer, W.G. and Dyer, J.H., 2013. Team building: Proven strategies for improving team performance. John Wiley & Sons.
Firestone, W.A., 2014. Teacher evaluation policy and conflicting theories of motivation. Educational researcher, 43(2), pp.100-107.
Graham, S. and Weiner, B., 2012. Motivation: Past, present, and future.
